An elevated Command Prompt is required before executing certain commands in Windows 7. The sfc command comes to mind, as does manage-bde, reagentc, and a few other Windows 7 commands.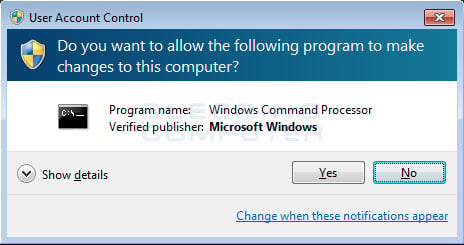

- Click on the Start button and in the Search programs and files box that appears directly above the Start button, type the following:
command
Don't press Enter, just let the search results populate above.
Note: If you have trouble doing this, or the next step, you can find the Command Prompt shortcut manually by clicking Start -> All Programs -> Accessories on most computers. Then skip to Step 3 below.
- In the search results, locate the Programs section.
Under Programs you'll see one or more programs listed that contain the word command.
- Locate the Command Prompt shortcut and right-click on it.
This will bring up Command Prompt's right-click menu. Depending on the software you have installed, and how you have certain Windows 7 settings configured, you could have as few as a dozen, or as many as a few dozen, options.
- Click on Run as administrator.
- Click Yes on the User Account Control window that appears.
Important: If you are see a User Account Control window but also a message that says To continue, type an administrator password, and then click Yes, then your user account must be a standard account, not an administrator account. Before you can click Yes and open an elevated command prompt, you'll need to type the password of another user on your Windows 7 computer that has administrator level privileges.
Note: You will not see this window at all if your User Account Control settings are turned all the way down. See How To Disable User Account Control in Windows 7 for more information.
- An elevated Command Prompt window will appear. You can now execute any Windows 7 command you want, without restriction.
Note: An elevated Command Prompt window opens to C:\Windows\system32. A non-elevated Command Prompt window instead opens to C:\Users\[username].
No comments:
Post a Comment